Jeżeli chodzi o beta-alanine ‘podstawy’ można przeczytac tutaj:
BETA-ALANINA – podstawy
Istnieje wiele podobieństw między BA a najlepszym ergogenikiem kreatyną.
Choć BA nie można jednoznacznie porównać z kreatyną, to wiele ‘cech’ mają podobnych:
-większa ilość karnozyny znajduje się we włóknach typu II (szybkokurczliwych) podobnie jak kreatyna
-podobnie jak kreatyna – karnozyna jest magazynowana w mięśniach -> czyli ich działanie faktyczne odczuje się po kilku-kilkunastu dniach
-podobnie jak kreatyna – trochę czasu musi minąć, aby jej poziom w mięśniach spadł do stanu początkowego
-istnieje zróżnicowanie jeśli chodzi o odczucia (osoby słabo i dobrze reagujące)
-poziom zależy od dawkowania
W tym temacie zajmę się 2 ostatnimi punktami ->
-skutecznymi dawkami
&
-zróznicowniem odczuć
***********************************************
The absorption of orally supplied beta-alanine and its effect on muscle carnosine synthesis in human vastus lateralis.
Beta-alanine in blood-plasma when administered as A) histidine dipeptides (equivalent to 40 mg . kg(-1) bwt of beta-alanine) in chicken broth, or B) 10, C) 20 and D) 40 mg . kg(-1) bwt beta-alanine (CarnoSyn, NAI, USA), peaked at 428 +/- SE 66, 47 +/- 13, 374 +/- 68 and 833 +/- 43 microM. Concentrations regained baseline at 2 h. Carnosine was not detected in plasma with A) although traces of this and anserine were found in urine. Loss of beta-alanine in urine with B) to D) was <5%. Plasma taurine was increased by beta-alanine ingestion but this did not result in any increased loss via urine. Pharmacodynamics were further investigated with 3 x B) per day given for 15 d. Dietary supplementation with I) 3.2 and II) 6.4 g . d(-1) beta-alanine (as multiple doses of 400 or 800 mg) or III) L-carnosine (isomolar to II) for 4 w resulted in significant increases in muscle carnosine estimated at 42.1, 64.2 and 65.8%
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16554972?dopt=Abstract&holding=f1000,f1000m,isrctn
suplementacja beta-alaniną przez 4 tygodnie:
– w ilości 3,2g skutkowała wzrostem karnozyny o 42.1
– w ilości 6,4g skutkowała wzrostem karnozyny o 64.2%.
beta-Alanine supplementation augments muscle carnosine content and attenuates fatigue during repeated isokinetic contraction bouts in trained sprinter
Carnosine (beta-alanyl-l-histidine) is present in high concentrations in human skeletal muscle. The ingestion of beta-alanine, the rate-limiting precursor of carnosine, has been shown to elevate the muscle carnosine content. We aimed to investigate, using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (proton MRS), whether oral supplementation with beta-alanine during 4 wk would elevate the calf muscle carnosine content and affect exercise performance in 400-m sprint-trained competitive athletes. Fifteen male athletes participated in a placebo-controlled, double-blind study and were supplemented orally for 4 wk with either 4.8 g/day beta-alanine or placebo. Muscle carnosine concentration was quantified in soleus and gastrocnemius by proton MRS. Performance was evaluated by isokinetic testing during five bouts of 30 maximal voluntary knee extensions, by endurance during isometric contraction at 45% maximal voluntary contraction, and by the indoor 400-m running time. beta-Alanine supplementation significantly increased the carnosine content in both the soleus (+47%) and gastrocnemius (+37%). In placebo, carnosine remained stable in soleus, while a small and significant increase of +16% occurred in gastrocnemius. Dynamic knee extension torque during the fourth and fifth bout was significantly improved with beta-alanine but not with placebo. Isometric endurance and 400-m race time were not affected by treatment. In conclusion, 1) proton MRS can be used to noninvasively quantify human muscle carnosine content; 2) muscle carnosine is increased by oral beta-alanine supplementation in sprint-trained athletes; 3) carnosine loading slightly but significantly attenuated fatigue in repeated bouts of exhaustive dynamic contractions; and 4) the increase in muscle carnosine did not improve isometric endurance or 400-m race time.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17690198
2 grupy pływaków:
-placebo
-przyjmująca beta-alanine (w ilości 2.4g/d przez 4 dni,3.6g/d prze kolejne 4dni,4.8g/d do końca 5 tygodnia)
Zawartość karnozyny w mięśniu płaszczkowatym – (przed/po):

-placebo 7.25/7.85 (+8%)
-BA 7.76/11.39 (+47%) ->maxymalnie aż 89%!
***********************************************
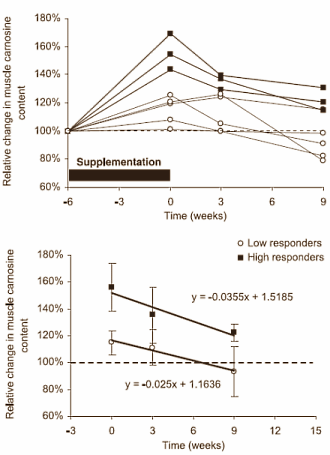
Również – podobnie jak w przypadku kreatyny – nie wszyscy odczują tak samo beta-alanine!
-Są osoby, które odczują bardzo dobrze
-Są osoby, które odczują słabo.
Carnosine loading and washout in human skeletal muscles.
Carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) is present in high concentrations in human skeletal muscles. The oral ingestion of beta-alanine, the rate-limiting precursor in carnosine synthesis, has been shown to elevate the muscle carnosine content both in trained and untrained humans. Little human data exist about the dynamics of the muscle carnosine content, its metabolic regulation, and its dependence on muscle fiber type. The present study aimed to investigate in three skeletal muscle types the supplementation-induced amplitude of carnosine synthesis and its subsequent elimination on cessation of supplementation (washout). Fifteen untrained males participated in a placebo-controlled double-blind study. They were supplemented for 5-6 wk with either 4.8 g/day beta-alanine or placebo. Muscle carnosine was quantified in soleus, tibialis anterior, and medial head of the gastrocnemius by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), before and after supplementation and 3 and 9 wk into washout. The beta-alanine supplementation significantly increased the carnosine content in soleus by 39%, in tibialis by 27%, and in gastrocnemius by 23% and declined post-supplementation at a rate of 2-4%/wk. Average muscle carnosine remained increased compared with baseline at 3 wk of washout (only one-third of the supplementation-induced increase had disappeared) and returned to baseline values within 9 wk at group level. Following subdivision into high responders (+55%) and low responders (+15%), washout period was 15 and 6 wk, respectively. In the placebo group, carnosine remained relatively constant with variation coefficients of 9-15% over a 3-mo period. It can be concluded that carnosine is a stable compound in human skeletal muscle, confirming the absence of carnosinase in myocytes. The present study shows that washout periods for crossover designs in supplementation studies for muscle metabolites may sometimes require months rather than weeks.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19131472
15 niewytrenownych osób przyjmowało 4,8g beta-alaniny przez okres 5-6tygodni
Naukowcy podzielili te osoby na:
-osoby dobrze reagowały – poziom karnozyny wzrósł średnio o ~55% (40-70%)
-osoby, które słabo reagowały – poziom karnozyny wzrósł średnio o ~15 (5-20%)
Kolejne podobieństwo do kreatyny?
http://www.sfd.pl/Kreatyna__osoby_odczuwaj%C4%85ce_dzia%C5%82anie_vs_osoby_nie_odczuwaj%C4%85cy_dzia%C5%82ania_-t704960.html
***********************************************
Effect of two β-alanine dosing protocols on muscle carnosine synthesis and washout.
Carnosine (β-alanyl-L: -histidine) is found in high concentrations in skeletal muscle and chronic β-alanine (BA) supplementation can increase carnosine content. This placebo-controlled, double-blind study compared two different 8-week BA dosing regimens on the time course of muscle carnosine loading and 8-week washout, leading to a BA dose-response study with serial muscle carnosine assessments throughout. Thirty-one young males were randomized into three BA dosing groups: (1) high-low: 3.2 g BA/day for 4 weeks, followed by 1.6 g BA/day for 4 weeks; (2) low-low: 1.6 g BA/day for 8 weeks; and (3) placebo. Muscle carnosine in tibialis-anterior (TA) and gastrocnemius (GA) muscles was measured by (1)H-MRS at weeks 0, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 16. Flushing symptoms and blood clinical chemistry were trivial in all three groups and there were no muscle carnosine changes in the placebo group. During the first 4 weeks, the increase for high-low (TA 2.04 mmol/kg(ww), GA 1.75 mmol/kg(ww)) was ~twofold greater than low-low (TA 1.12 mmol/kg(ww), GA 0.80 mmol/kg(ww)). 1.6 g BA/day significantly increased muscle carnosine within 2 weeks and induced continual rises in already augmented muscle carnosine stores (week 4-8, high-low regime). The dose-response showed a carnosine increase of 2.01 mmol/kg(ww) per 100 g of consumed BA, which was only dependent upon the total accumulated BA consumed (within a daily intake range of 1.6-3.2 g BA/day). Washout rates were gradual (0.18 mmol/kg(ww) and 0.43 mmol/kg(ww)/week; ~2%/week). In summary, the absolute increase in muscle carnosine is only dependent upon the total BA consumed and is not dependent upon baseline muscle carnosine, the muscle type, or the daily amount of supplemented BA.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21847611
31 mężczyzn zostało podzielone na 3 grupy i przyjmowali:
1) 3,2g BA przez okres 4 tygodni + 1,6g BA przez okres kolejnych 4 tygodni (high-low)
2) 1,6g BA przez okres 8tygodni (low-low)
3) placebo
Po 0, 2, 4, 8, 12 i 16 tygodniach mierzyli poziom karnozyny w:
-mięśniu piszczelowym przednim (tibialis-anterior-TA)
-mięśniu brzuchatym łydki (gastrocnemius – GA)
Wyniki po 4 tygodniach:
-grupa 1) TA 2.04 mmol/kg(ww) i GA 1.75 mmol/kg(ww)
-grupa 2) TA 1.12 mmol/kg(ww) i GA 0.80 mmol/kg(ww)
-> czyli 2x więcej karnozyny było w grupie 1) (dawka 3,2g vs 1,6g)!
Końcowe wyniki:
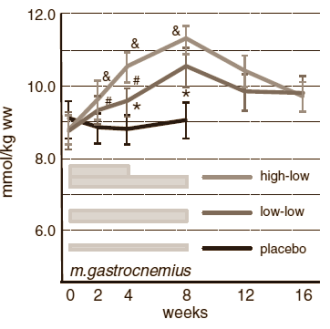
Należy zanotować fakt taki, że poziom karnozyny ciągle rósł!
Oczywiście spożywając 3,2g rósł szybciej niż spożywając 1,6g (2x szybciej).
Co ciekawe – zmniejszając dawkę o połowę (z 3,2g na 1,6g) po okresie 4 tygodni – poziom karnozyny dalej rósł!
Faza nasycenia?
Kolejne podobieństwo do kreatyny?
http://www.sfd.pl/Kreatyna__faza_%C5%82adowania_vs_bez_fazy_%C5%82adowania_%5D_Strategie_suplementacyjne_-t715385.html
Tak wiec widać, że podobnie jak w przypadku kreatyny – nie ma jednej drogi suplementacji:
-można spożywać większe dawki, jeżeli zależy nam na szybkości odczucia efektów
lub
-można spożywać mniejsze dawki – rozkładając efekty w czasie
lub
-zrobic (podobnie jak w przypadku kreatyny) fazę nasycania
Osoby, które mają odczuć beta-alanine odczują te sposoby dawkowania (przypominam ze część osób słabo odczuje).
Oczywiście stosując dawki minimalne (1-2g) efektów należy spodziewać się w dłuższej perspektywie niż spożywając 3-6g.
Wnioski końcowe naukowców:
Wzrost karnozyny w mięśniach jest uzależniony od ilości spożytej beta-alaniny (!) i nie jest zależny od początkowego poziomu karnozyny w mięśniach czy rodzaju mięśni.
Zapraszam do dyskusji na forum klikając TUTAJ
Autor: solaros (sfd)