Pewnie nie raz spotkaliscie sie z pytaniem – ile mogę dać maxymalnie białka w jednym posiłku?
Odpowiedź była z reguły 20-30g
Czy tak jest naprawdę?
I z reguły przytaczano to badanie:
Ingested protein dose response of muscle and albumin protein synthesis after resistance exercise in young men
BACKGROUND: The anabolic effect of resistance exercise is enhanced by the provision of dietary protein.
OBJECTIVES: We aimed to determine the ingested protein dose response of muscle (MPS) and albumin protein synthesis (APS) after resistance exercise. In addition, we measured the phosphorylation of candidate signaling proteins thought to regulate acute changes in MPS.
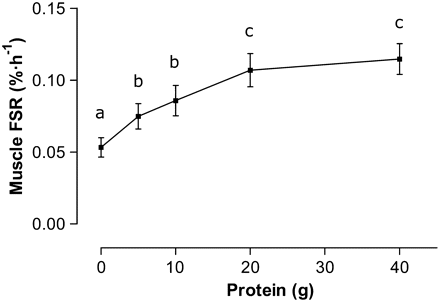
DESIGN: Six healthy young men reported to the laboratory on 5 separate occasions to perform an intense bout of leg-based resistance exercise. After exercise, participants consumed, in a randomized order, drinks containing 0, 5, 10, 20, or 40 g whole egg protein. Protein synthesis and whole-body leucine oxidation were measured over 4 h after exercise by a primed constant infusion of [1-(13)C]leucine.
RESULTS: MPS displayed a dose response to dietary protein ingestion and was maximally stimulated at 20 g. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (Thr(389)), ribosomal protein S6 (Ser(240/244)), and the epsilon-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (Ser(539)) were unaffected by protein ingestion. APS increased in a dose-dependent manner and also reached a plateau at 20 g ingested protein. Leucine oxidation was significantly increased after 20 and 40 g protein were ingested.
CONCLUSIONS: Ingestion of 20 g intact protein is sufficient to maximally stimulate MPS and APS after resistance exercise. Phosphorylation of candidate signaling proteins was not enhanced with any dose of protein ingested, which suggested that the stimulation of MPS after resistance exercise may be related to amino acid availability. Finally, dietary protein consumed after exercise in excess of the rate at which it can be incorporated into tissue protein stimulates irreversible oxidation.
[http://www.ajcn.org/content/89/1/161.full]
Po treningu podano odpowiednio dawkę 5, 10 , 20 i 40g zawierającą albuminy jajka
po 4h zaobserwowano, że dawka 20g była najbardziej optymalna
kiedy to miedzy 20 a 40g nie było znaczącej różnicy
….i wszystko powinno byc jasne.
Ale czy na pewno?
Czy ilość białka ma znaczenie?
Czy w ogóle ma znaczenie ile spożyjemy w 1 posiłku – mając w myślach calodzienne zapotrzebowanie?
A czy nie ma znaczenia waga osobnika?
czyli 100kilowy facet może spożyć 20g – tyle samo co jego 40kilowa narzeczona?
Czy nie liczy sie co jedlismy wczesniej?
To, że spożyliśmy kilka wielkich ciężkostrawnych posiłków którymi nam sie jeszcze odbija – będzie adekwtne do stanu rano naczczo, albo po długotrwałym poście?
I może najważniejsze – czy nie liczy sie źródło tego białka?
Jeżeli spożyjemy 20g białka z hydrolizatu białka – będzie trawił się tyle samo jeśli spożyjemy 20g białka z jaj?
Wszystko sie liczy i to bardzo!
Część osób ze wzgledu na TEF (ang. Thermogenic Effects of Food – termogeniczne działanie pokarmów) – poleca zwiększyć ilosc posiłków zawierających białko – kosztem ilości białka w 1 posiłku.
Według nich spożywając 30g białka 6x dziennie – podniesie bardziej TEF niz 3x60g.
Faktycznie?
Raczej nie – skoro TEF jest niezmienny (rozny dla bialka,weglowodanow i tluszczu) ale nie zmienny w czasie czy zalezby od gramatury posilkow.
TEF białek wynosi około 20 – 30%, oznacza to, że nawet do 30% energii pozyskiwanej z białka (jeśli zajdzie taka potrzeba, by przerabiać białko na energię) będzie zużyte na „przerobienie” białek do formy energii użytecznej dla organizmu – glukozy.
Węglowodany pełnostrawne: TEF „pełno strawnych” węglowodanów (skrobia, glukoza, fruktoza, sacharoza) wynosi około 7-10%
Tłuszcze: TEF tłuszczy jest wyjątkowo niski, wynosi zaledwie 2-3%
czyli spozywaqjac 6x30g bialka dostarcze 720kcal – TEF = 144kcal
a spozywajac 3x60g bialka dostarcze……
hmmmmmm?
3x60g=720g*4kcal*20%(TEF)=144kcal
…..tyle samo!
Wiec to ze spozywajac czesciej zwiekszymy TEF jest raczej nie prawda – bo te nie zmieni sie jesli spozyjemy tyle samo bialka.
To moze taki powod ze jezeli spozyjemy wiecej niz 20-30g zostanie zmarnowane?
Jesli zyskujemy tylko do 20g – to co sie stanie jesli spozyjemy 40g,a co jesli 50g bialka w 1 posilku?
Protein Feeding Pattern Does Not Affect Protein Retention in Young Women
This study was undertaken to determine whether a pulse protein feeding pattern was more efficient than a spread pattern to improve protein anabolism in young women as was already shown in elderly women. After a 15-d adaptive period [1.2 g protein/(kg fat-free mass · d)], 16 young women (age 26 ą 1 y) were given a 14-d diet providing 1.7 g protein/(kg fat-free mass · d), using either a pulse pattern (protein consumed mainly in one meal, n = 8), or a spread pattern (spreading daily protein intake over four meals, n = 8). Nitrogen balance was determined at the end of both the 15-d adaptive and the 14-d experimental periods. Whole-body protein turnover was determined at the end of the 14-d experimental period using [15N]glycine as an oral tracer. Nitrogen balance was 17 ą 5 mg N/(kg fat-free mass · d) during the adaptive period. It was higher during the experimental period, but not significantly different in the women fed the spread or the pulse patterns [59 ą 12 and 36 ą 8 mg N/(kg fat-free mass · d) respectively]. No significant effects of the protein feeding pattern were detected on either whole-body protein turnover [5.5 ą 0.2 vs. 6.1 ą 0.3 g protein/(kg fat-free mass · d) for spread and pulse pattern, respectively] or whole-body protein synthesis and protein breakdown. Thus, in young women, these protein feeding patterns did not have significantly different effects on protein retention.
[jn.nutrition.org/content/130/7/1700.short]
badano wplyw ilosci sposobu przyjmowania bialka na lodych kobietach.
kobiety mialy do spozycie 1,7g/kgmc w ciagu dnia
jedna grupa spozywala 4 posilki dajace w sumie 1,7g/kgmc
druga grupa spozywala 1 posilek zawierajacy 1,7g/kgmc
po 14 dniach sprawdzono bilans azostowy jak i zmiany w kompozycji ciala
wynik?
nie bylo wiekszych istatnych roznic zarowno w bilansie azotowym – ktory w obu grupach byl pozytywny i wynosil 59 vs.36, jak rowniez przemiany bialkowe wynosily 5,5 vs. 6,1.
Zadnych roznic!
jak rowniez tutaj:
Protein pulse feeding improves protein retention in elderly women.
BACKGROUND: Adequate protein nutrition could be used to limit gradual body protein loss and improve protein anabolism in the elderly.
OBJECTIVE: We tested the hypothesis that an uneven protein feeding pattern was more efficient in improving protein anabolism than was an even pattern.
DESIGN: After a controlled period, 15 elderly women (mean age: 68 y) were fed for 14 d either a pulse diet (n = 7), providing 80% of the daily protein intake at 1200, or a spread diet (n = 8), in which the same daily protein intake was spread over 4 meals. Both diets provided 1.7 g protein x kg fat-free mass (FFM)(-1) x d(-1). Protein accretion and daily protein turnover were determined by using the nitrogen balance method and the end product method (ammonia and urea) after an oral dose of [15N]glycine.
RESULTS: Nitrogen balance was more positive with the pulse than with the spread diet (54 +/- 7 compared with 27 +/- 6 mg N x kg FFM(-1) x d(-1); P < 0.05). Protein turnover rates were also higher with the pulse than with the spread diet (5.58 +/- 0.22 compared with 4.98 +/- 0.17 g protein x kg FFM(-1) x d(-1); P < 0.05), mainly because of higher protein synthesis in the pulse group (4.48 +/- 0.19 g protein x kg FFM(-1) x d(-1)) than in the spread group (3.75 +/- 0.19 g protein x kg FFM(-1) x d(-1)) (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION: A protein pulse-feeding pattern was more efficient than was a protein spread-feeding pattern in improving, after 14 d, whole-body protein retention in elderly women.
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10357740]
podobna zasada jak poprzednio – tym razem u starszych kobiet
ktere spozywaly 1,7g bialka na kgmc w 1 posilku lub w 3
wynik?
Tym razem bilans azotowy byl bardziej pozytywny u grupy spozywajacej 1 posilek (54) niz u grupy spozywajacej 4 posilki (27)
Synteza bialka u grupy spozywajacej 1 posilek wynosila 4,48 kiedy u grypu spozywajacej 4 posilki 3,75
wniosek?
spozycie 1 posilku dostarczjacego calodzienne zapotrezbowanie na bialko bylo lepsze niz spozycie 4 posilkow zawierajacy tyle samo bialka
Kolejna sprawa – zródla bialka-> dlugość trawienia
czy nie ma wogole znaczenia?
Czy jesli chodzi nie tylko o bialko ale jesli dieta zbilansowana nawet:
Splanchnic and leg substrate exchange after ingestion of a natural mixed meal in humans.
The disposal of a mixed meal was examined in 11 male subjects by multiple (splanchnic and femoral) catheterization combined with double-isotope technique (intravenous [2-3H]glucose plus oral U-[14C]starch). Glucose kinetics and organ substrate balance were measured basally and for 5 h after eating pizza (600 kcal) containing carbohydrates 75 g as starch, proteins 37 g, and lipids 17 g
After meal ingestion, there was a net leg uptake of BCAA (20+/-6 micromol x leg(-1) x min(-1)), whereas leg release of N-BCAA decreased by 50%. It is concluded that in human subjects, 1) the absorption of a natural mixed meal is still incomplete at 5 h after ingestion; 2) HGP is only marginally and tardily inhibited; 3) splanchnic and peripheral tissues contribute to the disposal of meal carbohydrate to approximately the same extent; 4) the splanchnic area transfers >30% of the ingested proteins to the systemic circulation; and 5) after meal ingestion, skeletal muscle takes up BCAA to replenish muscle protein stores.
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10331398]
po spozyciu pizzy (600kcal) posilek nadal byl trawiony po uplywie 5h!
Tak wiec jesli zjemy pizze to za 3 h musimy zjesc posilek zawierajacy kolejne 30g bialka,po kolejnych 3h tez?
mozemy ale ten czas trawienia jeszcze bardziej sie wydluzy!
Noie jest podane ile – ale na pewno nie jest jak sugeruje 1-wsze badanie ze zostnie nuzyte tylko 20g.
Tak – moze byc wykorzystne tylko 20g ale to bedzie zalezec od wielu czynnikow.
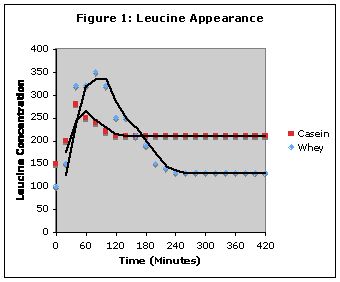
The digestion rate of protein is an independent regulating factor of postprandial protein retention.
To evaluate the importance of protein digestion rate on protein deposition, we characterized leucine kinetics after ingestion of „protein” meals of identical amino acid composition and nitrogen contents but of different digestion rates. Four groups of five or six young men received an L-[1-13C]leucine infusion and one of the following 30-g protein meals: a single meal of slowly digested casein (CAS), a single meal of free amino acid mimicking casein composition (AA), a single meal of rapidly digested whey proteins (WP), or repeated meals of whey proteins (RPT-WP) mimicking slow digestion rate. Comparisons were made between „fast” (AA, WP) and „slow” (CAS, RPT-WP) meals of identical amino acid composition (AA vs. CAS, and WP vs. RPT-WP). The fast meals induced a strong, rapid, and transient increase of aminoacidemia, leucine flux, and oxidation. After slow meals, these parameters increased moderately but durably. Postprandial leucine balance over 7 h was higher after the slow than after the fast meals (CAS: 38 +/- 13 vs. AA: -12 +/- 11, P < 0.01; RPT-WP: 87 +/- 25 vs. WP: 6 +/- 19 micromol/kg, P < 0.05). Protein digestion rate is an independent factor modulating postprandial protein deposition.
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11158939]
spozywano posilki zawierajace 30g bialka w postaci
-kazeiny
-aminokwasow (AA)
-wpc (?)
-wpc*n (kilka dawek wpc)
badana zawartosc leucyny po 7h po spozyciu kazeiny vs. AA i WPC vs. WPC*n
wyniki:
kazeina 38 vs. AA -12
wpc*n 87 vs. WPc 6
Wnioski:
Trawienie białka jest zależne od źródła i w zależności od tego źródła jest inna zawartość białka
Podsumowujac:
Limitem na pewno nie jest 30g a tymbardziej 20g.
Limitem jest/może być całodzienne zapotrzebowanie!
Ale tu bardzo istotnym aspektem jest łatwość czy ilość spożytego białka w zależności od wagi – łatwiej kobiecie dostarczyć 40g (jesli zamierzy dostarczyć 0,8g według RDA) niż facetowi podchodzacemu poważnie to tego sportu 2,2g w jednym posiłku – ale jest to też możliwe.
Może nie w 1 posiłku – ale przez okres kilku godzin – na przyklad 2-3 posiłki przez 4-6h przed/po treningu
Odpowiedź nie jest prosta a tymbardziej niejednoznaczna – ale nie pewno nie jest nia 20-30g na posiłek!
Dużo zależy od dziennego zapotrzebowania, jak również od kompozycji posiłków, czasu trawienia, wagi, wieku, płci, etc.
Zapraszam do dyskusji na forum klikając TUTAJ
Autor: solaros (sfd)








Świetny artykuł!
Teraz będę wiedział, że nie muszę rozbijać kostki twarogu na kilka części i chodzić nienajedzony 😀
Jajecznica z 7 jajek jak myślałem do tej pory – nie była chyba wcale tak głupim pomysłem. Dzięki !